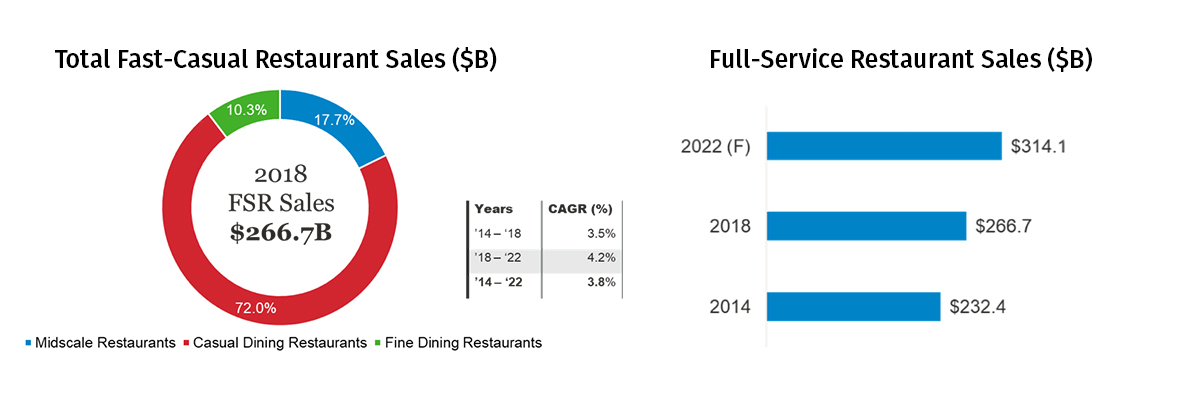
The full-service restaurant segment was valued at $266.7B in 2018 and is primarily composed of three subsegments:
midscale restaurants,
casual dining restaurants, and
fine dining restaurants.
The casual dining restaurant forms the largest subsegment of the full-service restaurant industry taking up 72% of all sales in this segment in 2018. Midscale restaurants follow suit, making up around 18% of the total sales. The fine dining segment, the smallest out of the three, made up roughly 10% of all full service restaurant sales in 2018.
The full-service restaurant industry grew by about 3.5% compounded annually between the years 2014 and 2018. It is expected to grow at a slightly higher compounded growth rate at 4.2% annually going into 2022; the total sales in 2022 are expected to reach $314.1B.
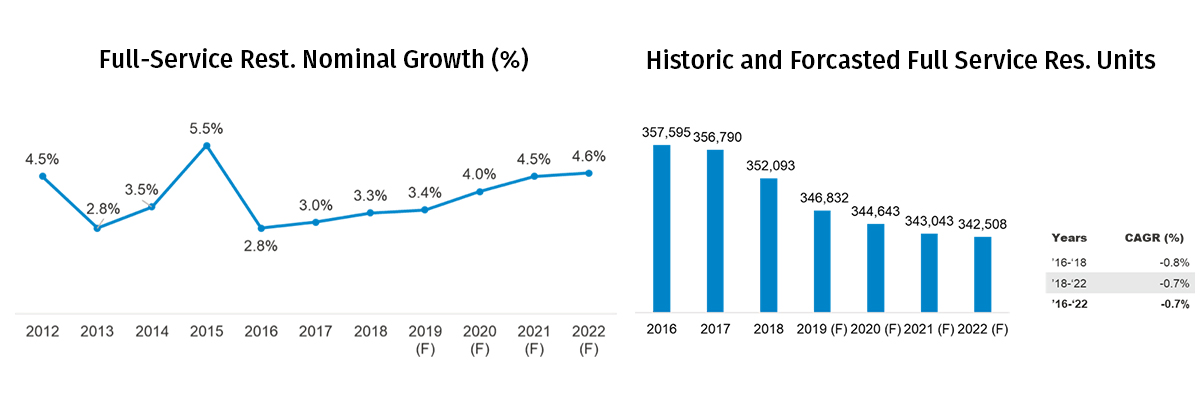
Historically, the segment has seen modest growth rates, especially compared to the limited-service segment. Growth peaked at 5.5% in 2015 before dropping down to 2.8% the following year. Growth rate recovered somewhat in 2018 reaching 3.3%. Looking ahead, the growth rates are expected to be higher than the current ones.
The full-service segment has seen a steady decline in the number of units between 2016 and 2018; units decreased by over 5,000 in this period. The number of units are expected to continue declining into 2022 at a compounded annual rate of 0.7%. This is driven largely by saturation of units in the full service restaurant industry and a shake-out of underperforming operations.
FSR Casual Dining Restaurants
Key Segment Metrics
The
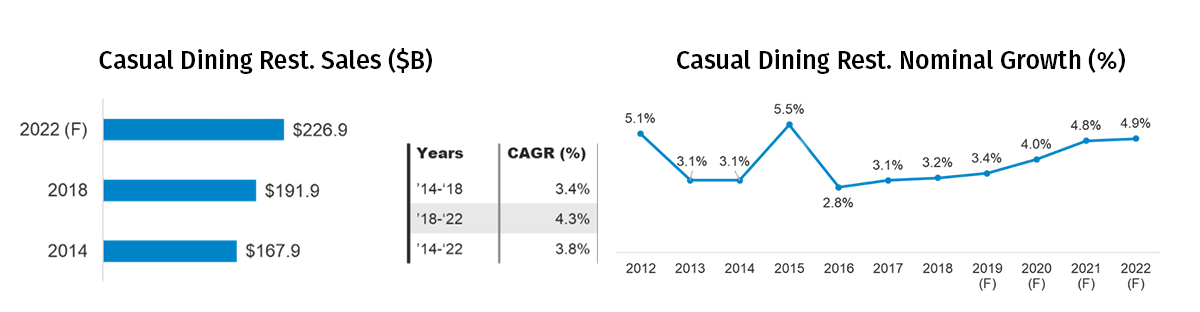
casual dining segment makes up the largest share of the full-service restaurant segment and amassed $191.9B worth of sales in 2018. Between 2014 and 2018, the segment grew by a compounded growth rate of 3.4% annually. By 2022, the segment's sales are expected to reach $226.9B and the casual dining segment is expected to grow at a slightly higher compounded growth rate of 4.3% annually.
Historically, the segment has seen variations in its growth levels. Growth rate decreased in 2013 from 5.1% to 3.1% before recovering back to 5.5% in 2015. Post-2015, the growth rate declined to 3.2% in 2018. The segment is expected to grow at an increasing rate from 2018 onwards, with growth rates reaching 4.9% by 2022.
The number of casual dining restaurant units have been decreasing from 2016, with the sharpest decrease in units occurring in 2018. The total number of units are expected to continue declining in 2019. Overall, by 2019, the segment is expected to lose nearly 10,000 units compared to 2016.
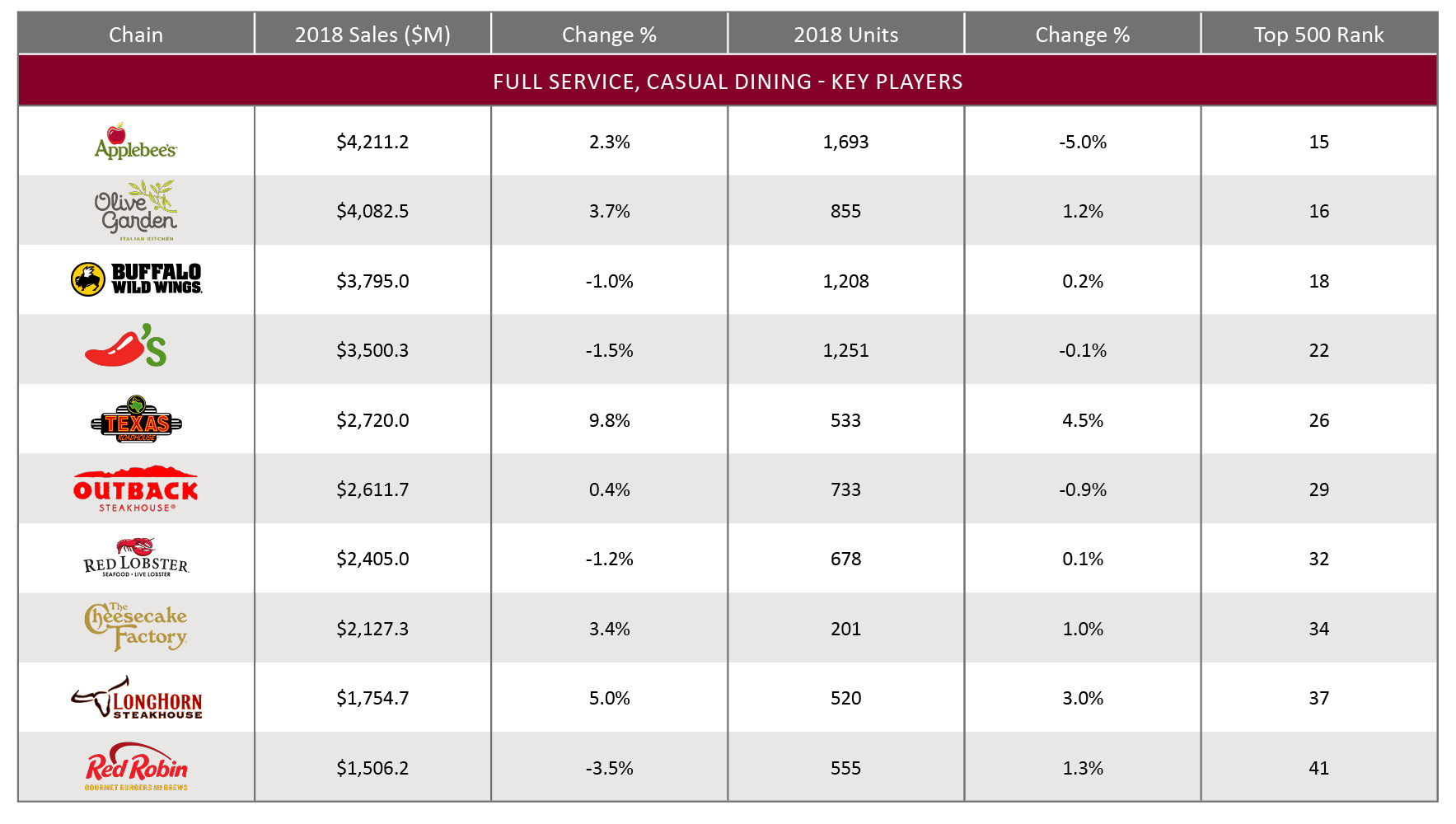
The following casual dining chains have been identified as the key players within this segment based on their total U.S. sales in 2018. Within the top ten chains, Texas Roadhouse grew its sales in 2018 at a significantly higher rate than other chains, emerging as a growth player in this segment. Most of the chains reported increases in their year-over-year sales as well as the units in 2018.

Key Segment Trends
- Large chain accounts have had challenges created a differentiated and unique experience, and chain growth is well below the growth of the independent casual dining operator. Independents tend to receive higher ratings from consumers specific to menu appeal, food and beverage quality, and overall ambience and experience.
- To appeal to health-conscious guests, expect more casual dining chains to capitalize on growing interest in functional fare. This could include highlighting antioxidants, vitamins and superfoods to convey meaningful benefits and natural remedies.
- Casual-dining chains, particularly those targeting younger consumers, may feel pressure to offer entertainment options. If brands choose to do so, they may do so in a way that matches a brand's positioning, such as family nights at a family-focused concept or sports gambling at a sports concept.
- Delivery and takeout are trending across the industry and FSRs are trying to adapt. However, off-premise occasions tend to challenge the typical FSR value proposition highlighting service and ambiance. As a result, FSRs can be expected to make continued investments in their off-premise programs, including packaging and digital ordering channels, to improve execution for off-premise orders.
- Within the casual dining segment, in addition to the traditionally loved and expected fare, the incorporation of ethnic items and spinning traditional fares with an ethnic flair are also emerging trends, as the segment moves to accommodate a generation with varying tastes.
Key Decision Makers
-
Owner–Owners of fast casual restaurants have the most important role in the decision to purchase and repair equipment.
-
General Manager–Oversees the day-to-day operations of restaurant stores. May not have a direct say in the equipment purchase but can escalate equipment related concerns to owner or area manager.
-
Chefs–play a secondary role as influencers; they often won't make the final decision but can have an impact on what is being evaluated.
-
Operations and facilities management – often larger chains have facilities or operations teams that get involved in equipment selection.
Role of Equipment Within the Segment
- As casual dining restaurants move to incorporate ethnic fares, the use of specialized equipment–spits, work ranges, tortilla makers, and chip warming cabinets, will support operators looking to add ethnic menu items.
- As casual dining restaurants have varied and extensive menu item offerings, versatility in cooking equipment is key so that multiple functions can be performed using the same equipment. For instance, two-sided commercial grills allow the same equipment to produce different items across dayparts.
- As an increasing number of casual dining restaurants offer delivery, the use of and need for heated holding cabinets and other heated solutions may become prominent so that casual dining restaurants can ensure that their food arrives to their customers without loss in quality.
FSR Midscale Restaurants
Key Segment Metrics
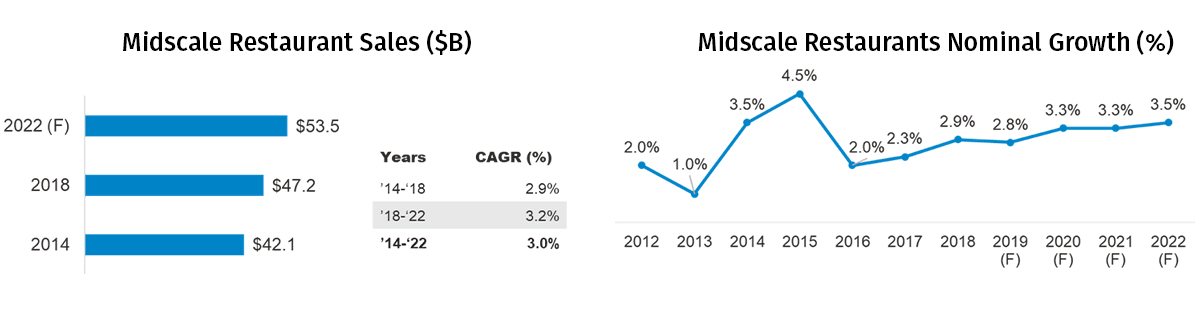
The midscale restaurant sales were worth $47.2B in 2018, an increase of $5.1B from 2014. During this period, the segment grew by a compounded annual growth rate of 2.9%. By 2022, sales in this segment are expected to be around $53.5B, growing at a slightly higher compounded annual growth rate of 3.2%. Historically, the segment has seen turbulent growth rates, with growth rates declining to 1% in 2013 before peaking at 4.5% in 2015. The midscale segment saw another period of slump in 2016 when growth rates plummeted to 2%. Since then, the growth rate has steadily increased to 2.9% in 2018. Looking ahead, the segment is expected to recover its growth rate incrementally reaching 3.5% in 2022.
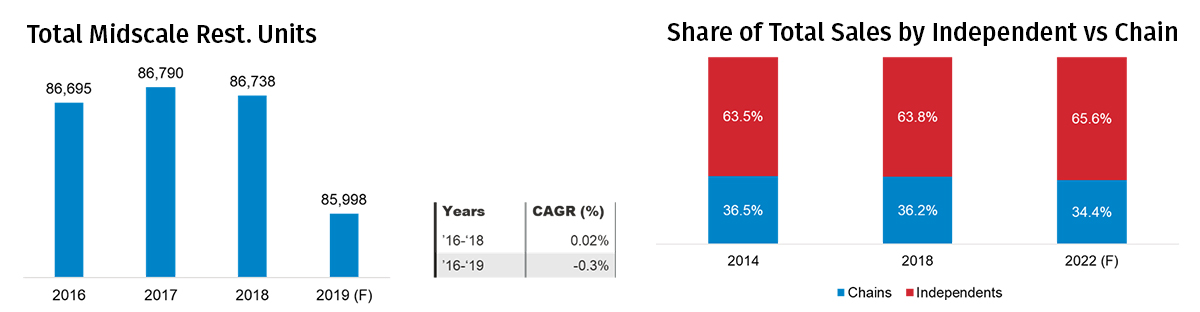
The number of midscale restaurant units increased between 2016 and 2017 before declining somewhat in 2018. In 2019, the number of units are expected to decline further.
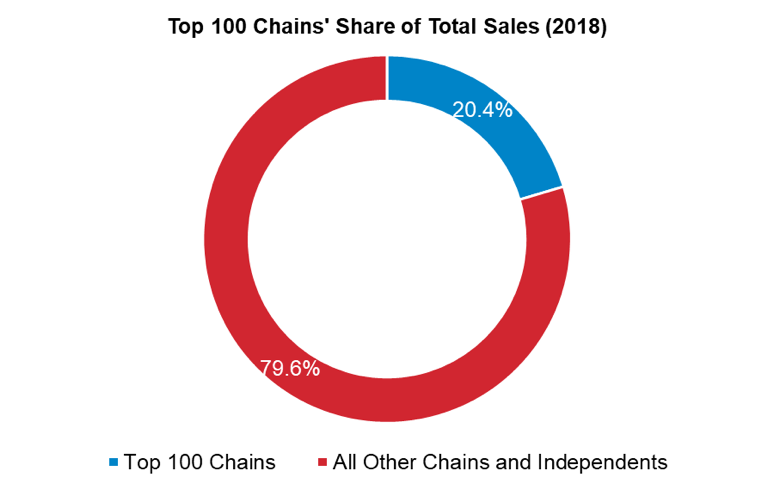
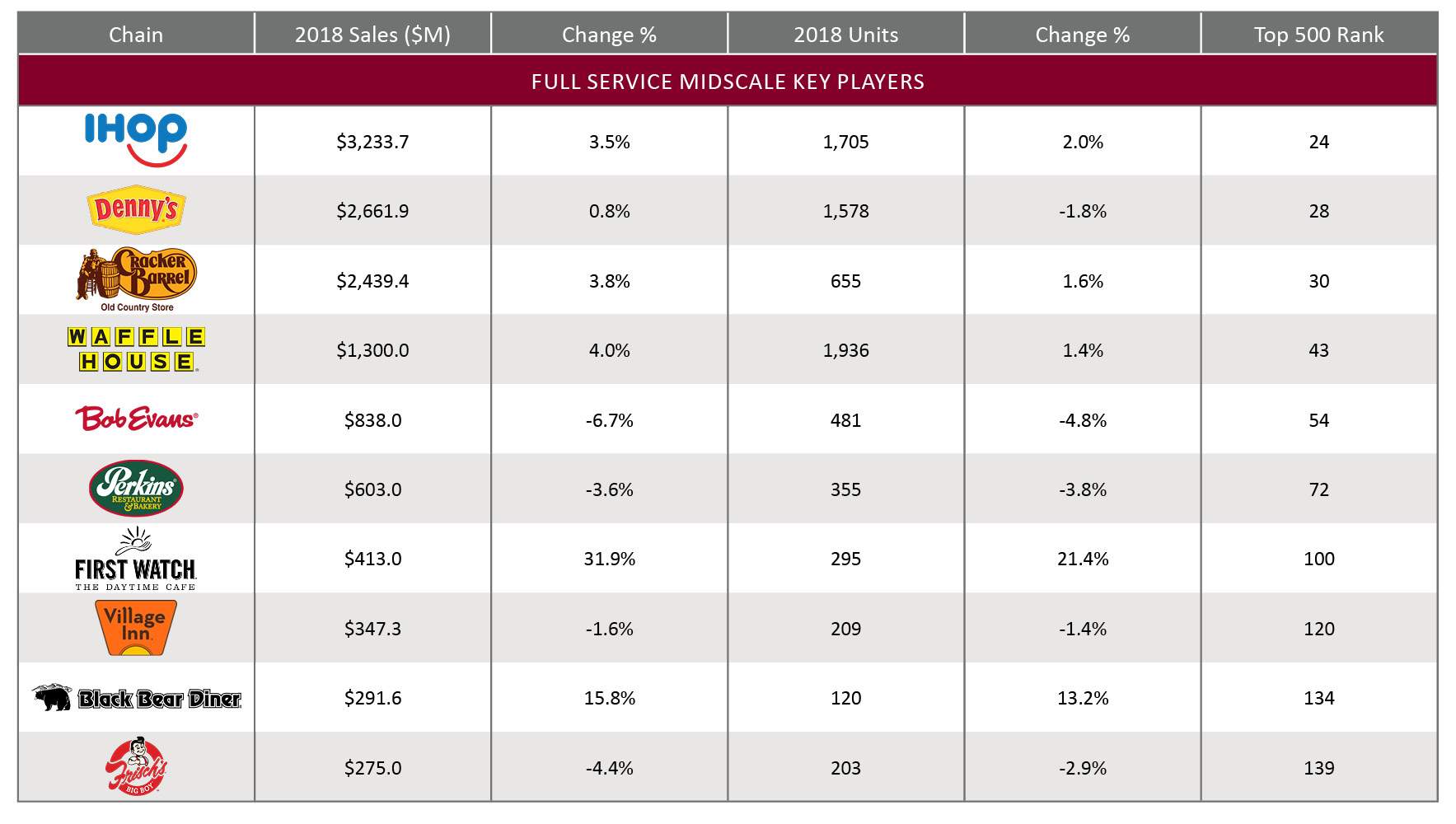
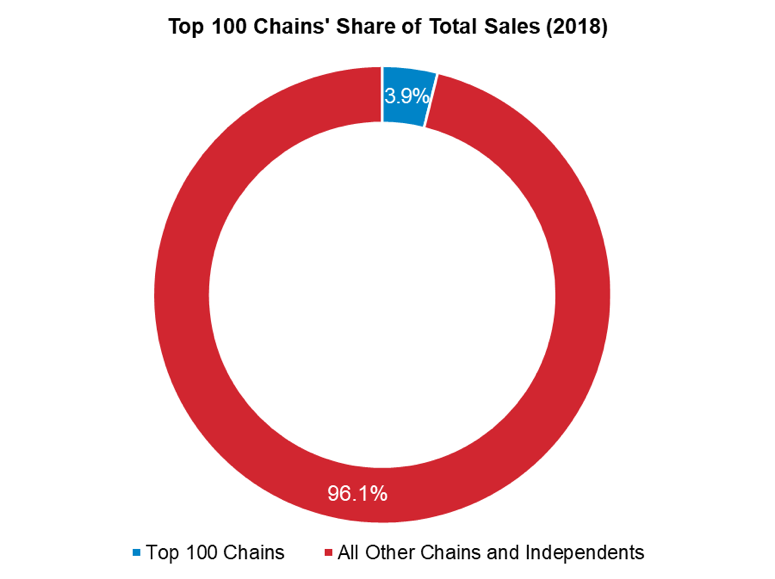
The table below identifies the key players in the midscale restaurant segment based on their total U.S. sales in 2018. Most of the top ten midscale chain restaurants reported year-over-year increase in their sales in 2018. Nevertheless, five of the top ten midscale restaurant chains experienced a decline in their number of units in 2018. In this segment, the top 100 chains held 23.9% of the segment's total sales in 2018.

Key Segment Trends
- Kids' increasingly sophisticated tastes drive menu decisions at family-style dining restaurants. To stay relevant with today's kids (and their foodie parents), restaurants are offering options that help kids expand their palates. An ethnic twist on a classic favorite or a dish of familiar ingredients prepared in a new way can provide options kids are excited to try.
- Children—both directly and, in particular, indirectly—strongly influence the decision-making process of picking a restaurant to eat at. Therefore, a focus on creating a memorable entertainment experience with games and play areas for kids are helping to keep restaurants top of mind and encourage kids to ask for repeat visits.
- Family-style restaurants have been traditionally associated with big plates and huge portions. However, an increasing number of family-style restaurants are also offering smaller or multiple shareable plates for the whole table to enjoy.
Key Decision Makers
- Owner–Owners of midscale restaurants have the most important role in the decision to purchase and repair equipment.
- Director of Operations–Function prominently in corporately owned and operated chains. Regional director of operations manages and coordinates the procedures for maintenance and purchase of equipment.
- Area Managers–Within corporately owned or operated chains, the area managers escalate equipment needs, issues, and concerns to upper management.
- General Manager–Oversees the day-to-day operations of restaurant stores. May not have a direct say in the equipment purchase but can escalate equipment related concerns to owner or area manager.
Role of Equipment Within the Segment
- As family dining restaurants have varied and extensive menu item offerings, versatility in cooking equipment is key so that multiple functions can be performed using the same equipment. For instance, two-sided commercial grills allow the same equipment to produce different items across dayparts.
- Family dining restaurants have larger portions and coupled with an extensive menu list mean that operators look for cooking and refrigeration equipment that is tailored to and suitable for a high-volume kitchen.
- Family-style restaurant diners looking for healthier options on the kids' menu can be satisfied by using equipment such as half-sized convection ovens that cater to a smaller serving size and serve as an alternative to traditionally deep-fried foods.
FSR Fine Dining Restaurants
Key Segment Metrics
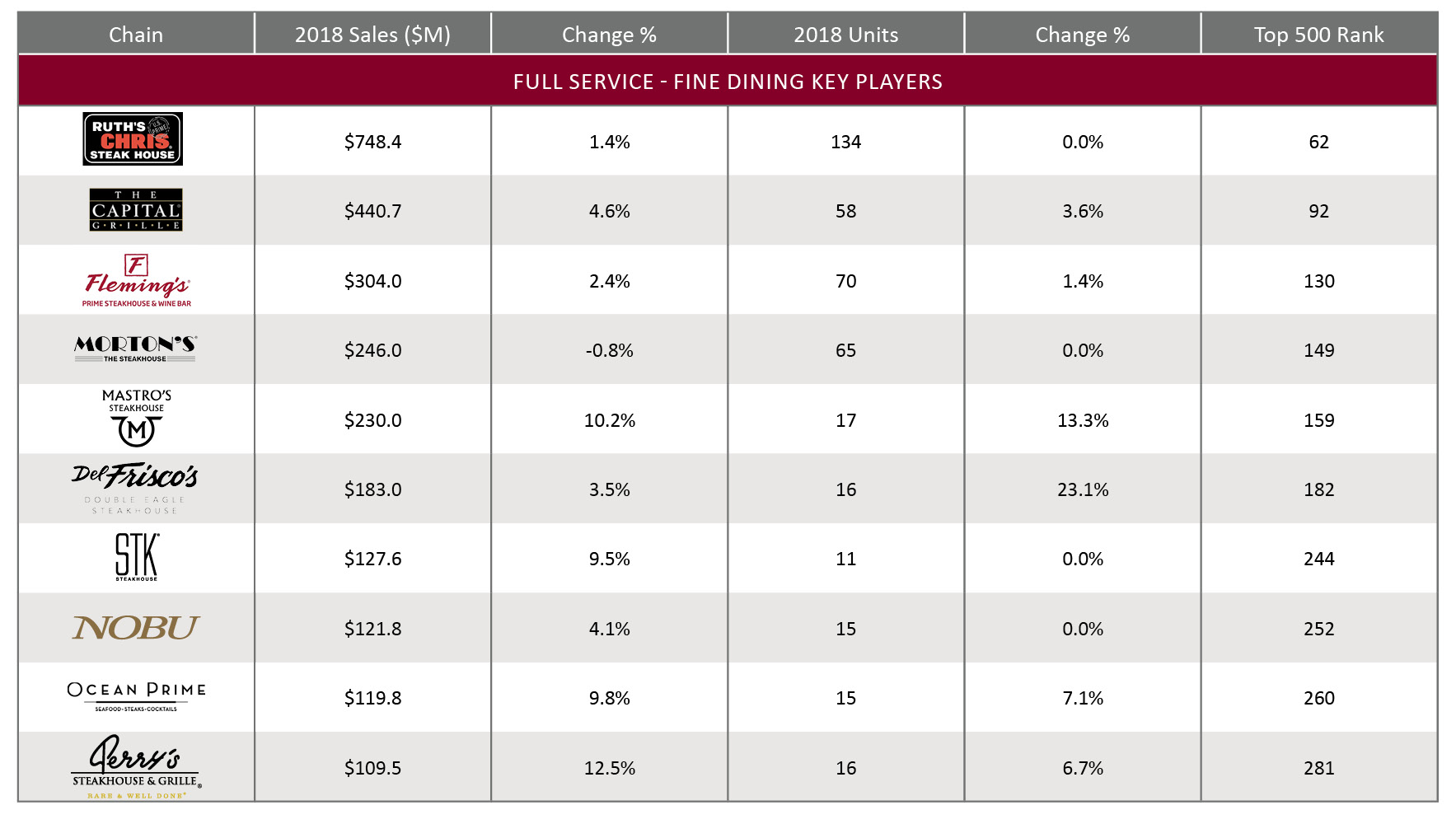
Fine dining, the smallest segment amongst all full service restaurant segments, had $27.6B sales in 2018, an increase of $5.2B from 2014. Between 2014 and 2018, the segment grew at a compounded growth rate of 5.4% annually. By 2022, the sales of fine dining segment are expected to increase to $33.6B, growing at a similar compounded growth rate of 5% annually. Historically, the segment reached its peak growth rate in 2015 as well, when the segment grew by 8.1%. Since then, the growth rates have faltered to 5% in 2018. Looking into 2022, the segment is expected to maintain growing at or around this rate. The fine dining segment is the fastest growing full-service restaurant segment.


Key Segment Trends
- Multi-sensory dining and chef's table experiences are predicted to move to the forefront in 2019 as premium restaurants focus on developing unique experiential offerings. Multisensory dining refers to the incorporation of ambient sights, sounds, and smells in addition to the food to drive up the overall experience of diners.
- Some fine dining restaurants are including elements of socializing and creating larger tables and welcoming groups during the slower hours of 4 p.m. to 6 p.m. and 10 p.m. to 1 a.m. This also includes a focus or re-emphasis on the bar, and often includes “bar menus" that include shareables and lower cost items to drive traffic in this area of the restaurant.
- Fine dining restaurants are moving away from overly fussy, finnicky, and overbearing service to one which is centered on warmth and genuine hospitality. Overall, the “casualization" of fine dining shows that many operators are trying to broaden the appeal of these types of restaurants.
- Emerging fine dining restaurants are leading the charge with more intimate, chef-led fine dining focusing on creative intimacy.
Key Decision Makers
- Owner–Owners of fine dining restaurants have the most important role in the decision to purchase and repair equipment.
- General Manager–Oversees the day-to-day operations of restaurants. May not have a direct say in the equipment purchase but can escalate equipment related concerns to owner or area manager.
- Chefs–may play a secondary role as influencers; they often won't make the final decision but can have an impact on what is being evaluated. Many fine dining establishments are chef-led and their influence and role will be more involved in such cases.
Role of Equipment Within the Segment
- As many fine-dining restaurants are smaller and/or open for fewer hours than restaurants in other segments, their cooking equipment needs will not be extensive, as they do not see a high-volume output in their kitchens.
- The role of equipment in the fine dining segment goes beyond that in the back-of-the-house. For fine dining restaurants aiming for a multi-sensory experience, the front-of-the-house equipment plays an important role to center the various senses of smell and sights and convey their concepts to guests.
- Larger fine dining restaurants with hundreds of seats per unit are making the use of more compact and more multipurpose equipment than those traditional fine dining restaurants used 10 years ago for greater efficiency and flexibility.